Automobile: Production is expected to recover, especially for HEVs and BEVs, which have received government support measures.
-
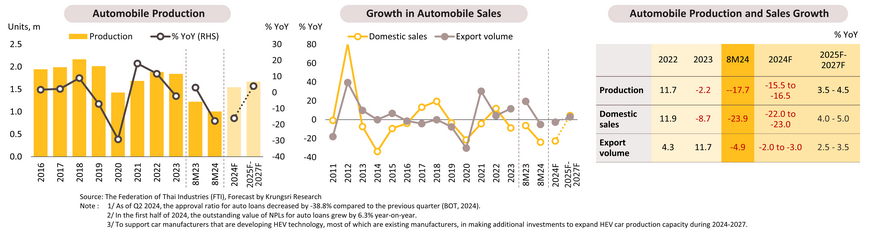
Auto production in 8M24 decreased by -17.7% YoY to 1,005,749 units, due to contractions in both domestic and export markets. The production of pickup trucks and passenger cars decreased by -22.3% YoY and -11.9% YoY, respectively, while the production of passenger HEVs and BEVs increased by 45.9% YoY and 3,857.4% YoY, respectively. Domestic sales dropped by -23.6% YoY to 399,611 units, with pickup truck and passenger car sales down -40.0% and -20.6% YoY, respectively. This decline is due to (i) weakened purchasing power from high living costs and the impact of El Niño on reduced agricultural output, (ii) stricter lending measures from financial institutions1/ to control NPLs on auto loans2/, and (iii) the continued decline in used car prices, causing some consumers to delay selling their old cars to purchase new ones. Exports decreased by -4.9% YoY to 688,633 units, due to the slow recovery of purchasing power in trading partner countries. However, some markets continued to show strong growth, including the US (+24.2% YoY), Saudi Arabia (+10.3% YoY), and Australia (+4.5% YoY). In 2024, production, domestic sales, and exports are expected to decline by -15.5% to -16.5%, -22.0% to -23.0%, and -2.0% to -3.0%, respectively.
-
During 2025-2027, production is expected to increase by an average of 3.5-4.5%, driven by (i) the easing of the chip shortage, with an increase in global chip supply, and (ii) BEV production in 2024-2025 and 2026-2027 under EV 3.0 and 3.5 support measures, respectively, to offset previous vehicle imports. Domestic sales are expected to grow by an average of 4.0-5.0% annually, supported by (i) a recovery in business activities, investment, and tourism sector, (ii) the onset of La Niña, which will boost agricultural output and increase demand for pickup trucks, and (iii) support measures for HEV sales through excise tax reductions3/. Exports are expected to increase by an average of 2.5-3.5% per year, driven by economic recovery and improved investment conditions in trading partner countries. The ASEAN market, in particular, will benefit from increased production investments from China and Japan to reduce risks from ongoing geopolitical conflicts.
Electric vehicles: Production and domestic sales of BEV and HEV are expected to increase due to government support measures.
-
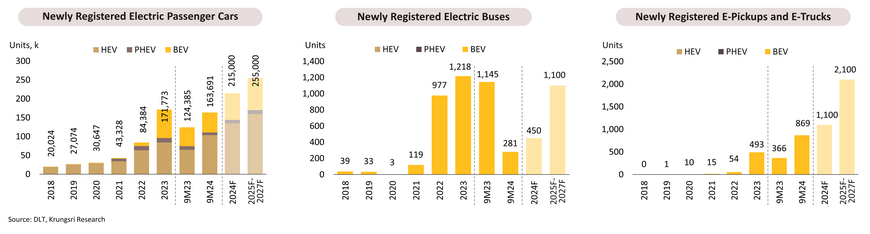
During 9M24, new registrations of passenger XEVs increased by 31.6% YoY to 163,691 units. This includes (i) passenger BEVs (+5.4% YoY to 52,702 units) driven by EV 3.0 and EV 3.5 measures, growing consumer understanding of BEV technology and environmental awareness, a variety of available models, and increased driving range; (ii) passenger HEVs (+59.9% YoY to 103,686 units), boosted by the popularity among middle-to-upper income consumers who are not yet ready to switch to 100% EVs and a variety of models available, especially from traditional Japanese manufacturers; and (iii) PHEVs (-23.3% YoY to 7,303 units), as the market continues to favor BEVs and HEVs, which are still supported by government policies. New registrations of BEV buses fell by -75.5% YoY to 281 units, following a surge in electric bus deployment over the past two years. Meanwhile, new registrations of commercial BEVs (pickups and trucks) increased by 137.4% YoY to 869 units, driven by recent advancements in battery technology that have extended driving ranges for commercial use. However, the registrations remain limited due to insufficient charging stations in rural areas. For the entire year of 2024, new registrations of XEVs are expected to reach 215,000 units, divided into 71,000 BEVs, 135,000 HEVs, and 9,000 PHEVs, respectively.
-
During 2025-2027, XEV production capacity is expected to reach approximately 500,000 units per year by 2027, aimed at offsetting electric vehicle imports under the EV 3.0 and EV 3.5 measures at 1-1.5 and 2-3 times, respectively. New registrations of BEVs, HEVs, and PHEVs are expected to increase by an average of 85,000, 160,000, and 10,000 units per year, respectively. This growth is supported by (i) EV 3.5 measures, (ii) excise tax reduction measures for HEVs, which will encourage the development of more efficient new models, (iii) the trend of increasing battery capacity leading to decreasing EV prices, (iv) the development of new BEV models, and (v) the implementation of Euro 6 standards in 2025, which will result in higher prices for ICE vehicles.
ICs and electrical appliances: Production and exports will gradually increase due to the upward cycle and investments in establishing production bases across the industry.
8M24
-
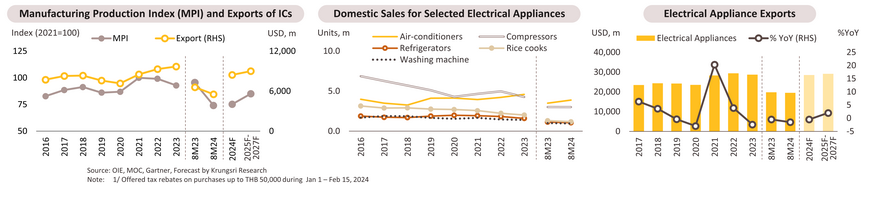
Integrated Circuits (ICs): Production and export value dropped by -22.5% and -15.9% YoY, respectively, due to delayed purchasing recovery amid global economic uncertainty, geopolitical conflicts, trade tensions, and technological barriers, especially between the US and China (which may continue to suppress demand for industries that rely on ICs), and the competition from China’s oversupplied exports. Thai IC exports to major markets, including the US and China, fell by -39.3% and -10.6% YoY, respectively, despite a global IC industry entering an upward cycle. For the entire year 2024, the production and export value of ICs are expected to decrease by -19.0% and -13.0%, respectively.
-
Electrical appliances: Domestic sales increased by 1.5% YoY, supported by the Easy E-Receipt scheme1/ and unusually hot weather that boosted air conditioner sales by 11.4% YoY. However, the burden of high household debt and cost of living has led to declines in sales of certain electrical appliances, such as refrigerators (-7.1% YoY), rice cookers (-5.9% YoY), and washing machines (-9.1% YoY). Meanwhile, export value has continued to decline by -1.5% YoY due to ongoing uncertainties in the global economy and persistently high energy costs. For the entire year of 2024, domestic sales are expected to grow by 1.5-2.5%, while export value is projected to decrease by -0.5% to -1.5% YoY.
2025-2027 Outlook
-
ICs: Production and exports will rise by respectively 10.0-15.0% and 6.5-7.5% YoY, driven by: (i) recovering global demand for ICs, projected to grow 5.8% annually from 2024-2033 (Precedence Research, 2024), especially in high-density interconnect and flexible PCBs; (ii) the upward cycle of PCs and smartphones (Gartner, 2024); (iii) increasing global demand for electric vehicles, with an 18.2% annual growth forecast from 2024-2030 (IEA,2024); and (iv) increased investment in smart electronics and midstream electronic components, particularly due to production base relocations away from China.
-
Electrical appliances: Domestic sales and export value are expected to grow by 1.5-2.0% YoY, driven by (i) the recovery of the economy, tourism, and real estate business; (ii) increased demand for premium appliances from middle- to upper-income consumers; (iii) a new cycle of appliance replacement since the COVID-19 crisis; and (iv) the gradual economic recovery in trading partner countries and the trend of gradual subsiding living costs.
Digital services and software: Revenue growth will be boosted by data-driven strategies in the business sector, with increased investment in cloud infrastructure and data center.
-
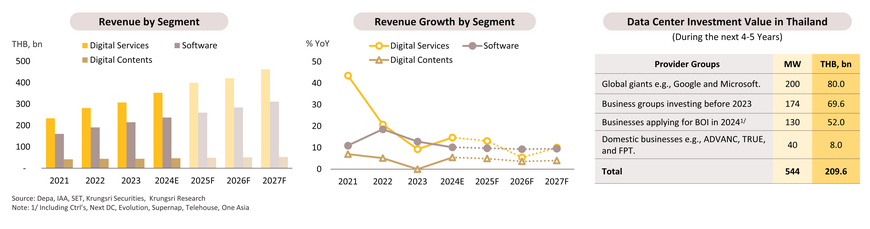
In 2024, overall revenue in Digital services, software, and digital content is projected to grow by 12.0-12.5%, up from 9.8% in 2023. Digital service revenue will increase by 14.5-15.0% (compared to 9.3% in 2023), with 60% coming from last-mile delivery and online retail, despite increased competition and thus slow growth. High-growth segments include platforms for e-tourism (boosted by tourism recovery), EdTech (reskilling/upskilling demand), and HealthTech (expanding advanced medical wearables whose growth averaged 60-70%). Software business is projected to grow by 10.0-10.5% in 2024 (down from 12.8% in 2023), driven by AI adoption in cloud databases and new software focused on data security. Increased SME investment in tailored website solutions is also boosting growth. Meanwhile, Digital Content is expected to rebound by 5.0-5.5% in 2024 (from only +0.01% in 2023), driven by the animation and character sectors, on a surge in promotional activities aligned with the ongoing growth in business and tourism. Revenue from new game programs is also recovering, with the increasing capabilities of smart devices and cloud systems.
-
Over 2025 - 2027, total revenue is expected to grow by 9.0-9.5% annually, with digital service revenue projected to expand by 9.5-10.0% per year, aligned with consumers increasingly favoring online transactions and further development of all-in-one service platforms. The market value of digital services related to retail, transportation, and online media in Thailand is anticipated to grow at an average of 15.3% per year from 2025 to 2027 (E-conomy SEA 2023 report). Software business revenue is expected to rise by 9.0-9.5%, driven by increased investment in cloud systems and data centers that support more efficient and cost-effective internet-based software services, aligning with businesses focusing on data as a key driver of their strategies. Meanwhile, digital content is expected to recover to 4.0-4.5%, with the gaming sector showing improved growth due to the development of new game formats on cloud gaming platforms compatible with various devices. Additionally, animation and character segments are likely to benefit from demand for licensing to produce goods that support the ongoing recovery in business and tourism.
Petrochemical: The sector is gradually recovering, but excess supply from Asian operators is limiting demand for Thai petrochemical products.
-
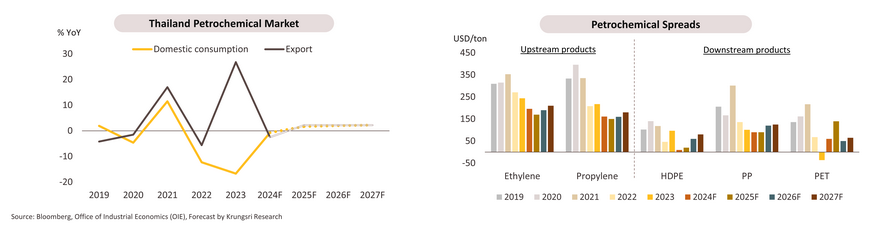
The domestic petrochemicals market continued to slow down over 8M24. Consumption fell -5.1% YoY due to weak manufacturing sectors, as reflected by the MPI contraction of -1.7% YoY. This caused a softening in the demand for petrochemical products as inputs in downstream manufacturing processes, such as packaging, electronics, and automotive. Meanwhile, export volumes contracted by -3.2% YoY, in line with the slowing economies of trading partners. Additionally, the competitiveness of Thai petrochemical products has decreased compared to China, the US, and the Middle East, which have expanded production capacity and possess lower production costs. For the rest of 2024, the petrochemical industry is expected to be supported by the tourism sector entering the year-end festival season, and the first phase of the digital wallet initiative. These are anticipated to stimulate spending in Q4. As a result, for 2024, domestic consumption is expected to contract by only -1.0% to -0.5% compared to 2023, while export volumes are projected to decrease by -3.0% to -2.0% due to the ongoing slowdown in demand from trading partners.
-
Over 2025 to 2027, domestic consumption is expected to gradually recover, driven by the growth of the Thai economy, particularly in the tourism sector. This will lead to increased demand for petrochemical products from downstream industries, especially in packaging. Additionally, businesses are likely to expand investments in products that meet global market demands, such as (i) high-value specialty plastic products, (ii) biodegradable plastics, (iii) the establishment of high-quality recycled plastic production plants with comprehensive capabilities meeting global standards, and (iv) the development of carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies that can use CO2 as a feedstock in the plastic production. However, the continued surplus supply from new production capacity expansions by operators in Asia will constrain the demand for Thai petrochemical products. Domestic consumption and export volumes will thus grow at an average rate of 1.5-2.5% per year.
Refinery: Rising oil demand, in line with Thailand's economic recovery, will boost GRMs to pre-pandemic levels.
-
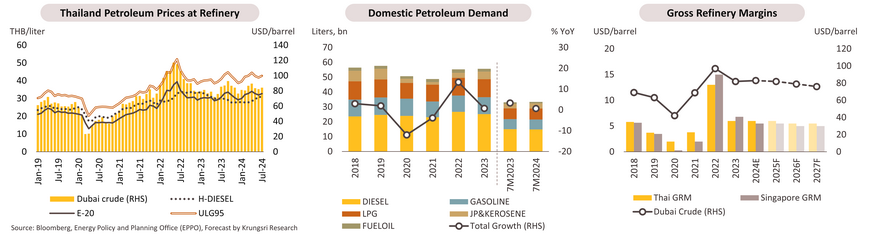
In 7M24, Gross refinery margins (GRMs) have been continuously declining due to the rising global crude oil prices, driven by conflicts in the Middle East and supply constraints imposed by OPEC+ to support prices. As a result, the average price of Dubai crude oil reached USD 83.6/bbl (+6.0% YoY), leading to increases in ex-refinery prices of petroleum products in Thailand, such as gasoline and E-20, by 6.0% and 7.8% YoY, respectively. However, domestic demand for finished oil products has increased only slightly by 0.7% YoY, reflecting a slowdown in the manufacturing and industrial sectors, evidenced by a decline in diesel and fuel oil demand of -1.4% and -18.8% YoY, respectively. For the remainder of the year, it is expected that the recovery of the tourism sector and the approach of the year-end festival season will lead to increased demand for oil in the transportation sector, helping to stabilize demand for finished oil products close to the same period in 2023. This will support a gradual improvement in GRMs, resulting in an average GRMs for 2024 at USD 4.5-5.0/bbl, compared to 6.0/bbl in 2023, with the average price of Dubai crude oil expected at USD 83/bbl.
-
In the years 2025-2027, refining margins are expected to increase, supported by the recovery of economic activities. The tourism sector remains a key driver of domestic oil demand. At the same time, global crude oil prices are anticipated to decline slightly due to the easing of conflicts in the Middle East, with the average price of Dubai crude expected to be USD 76-82/bbl. This is projected to allow Thailand’s GRMs to average between USD 5.0-6.0/bbl, close to levels seen before COVID-19. Additionally, oil refinery operators are likely to expand their revenue base, particularly through investments related to clean energy or by adding value to products, such as low-sulfur jet fuel. This aligns with government policies aimed at reducing air pollution and lowering greenhouse gas emissions to achieve net-zero targets.
Power Generation: Electricity demand is expected to keep growing, while operators expand their investments in green power plants.
-
Over 8M24, operators’ revenue has improved, driven by (i) a 9.8% YoY increase in household power consumption due to hot weather and reduced retail electricity prices, along with a 4.9% YoY rise in the business consumption (65.6% of total demand), supported by the recovery of tourism and exports, and (ii) a total of 61,155 newly registered BEVs and PHEVs in 9M24. Peak electricity demand reached a record 36,477.8 MW in April (+6.9% from the peak in 2023). For the remainder of the year, demand is expected to rise thanks to a recovery of exports and the high tourism season, leading to an overall increase of electricity demand of 5.0%-6.0% in 2024 compared to 3.4% in 2023. Additionally, renewable energy supply to the national grid is forecast to reach 10,300 MW (3.4% from 2023).
-
In 2025-2027, the industry is expected to grow gradually, with electricity demand increasing at an average rate of 5.0-6.0% per year. This growth is driven by (i) the continued recovery of the Thai economy, which supports electricity use in the business sector; (ii) rising temperatures (Thailand’s average temperature was 28.1°C in 2023, up from 27.4°C in 2022); and (iii) a projected annual 15.0% increase in BEVs and PHEVs registrations. The government will continue to support investments in power generation, particularly from renewable sources, in line with the PDP and AEDP. This will promote economic growth, the transition to clean energy, and investments in green power plants. The revenue and investment outlook for operators is summarized as follows:
-
IPPs: Income is expected to improve due to (i) recovering electricity demand aligned with economic recovery and (ii) expanded investments in (a) natural gas power plants in the northeast and south, and domestic renewables; (b) hydrogen power and energy storage; and (c) overseas solar and wind projects.
-
SPPs: Revenue is expected to grow gradually, with investment opportunities in (i) natural gas cogeneration plants with contracts expiring in 2025; (ii) hybrid renewable energy SPPs; and (iii) new power plants in the EEC.
-
VSPPs: Revenue and investment are expected to accelerate due to (i) the government's plan to purchase over 12,000 MW of renewable energy by 2027 and (ii) BOI tax incentives promoting clean energy. However, new operators may face raw material limitations, particularly for biomass and biogas plants.
Chilled, Frozen and Processed Chicken Industry: Domestic demand will be driven by the food services and tourism rebound, with exports stimulated by new market opportunities.
-
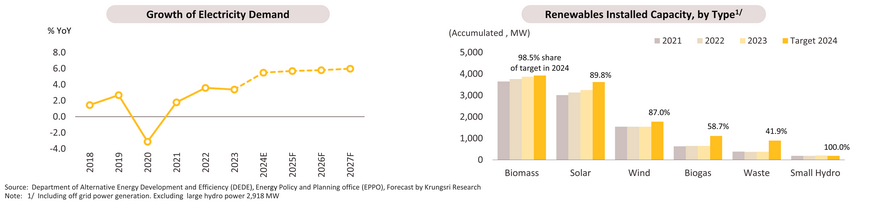
In 2023, Thailand's broiler production increased by 1.0% to 1.95 billion broilers, resulting in a 1.0% increase in chilled, frozen, and processed chicken outputs, which reached 3.15 million tons. This growth was primarily driven by persistently high retail prices of 43.5 baht per kilogram, encouraging farmers to raise more broilers. However, domestic consumption decreased by -1.9% to 2.07 million tons as consumers shifted to lower-priced meats and regained confidence in pork following a decline in swine disease concerns. Export volumes increased by 6.9% to 1.07 million tons, as chicken became an affordable protein source amidst a global economic slowdown, leading consumers to seek cheaper food options. Additionally, outbreaks of avian influenza in some countries prompted trade partners to increase chicken imports from Thailand. For 2024, production, consumption, and export volumes are expected to grow by 2.0-3.0%, 1.0-2.0%, and 4.0-5.0%, respectively.
-
Over 2025 to 2027, the output is expected to grow by 2.5-3.5% per year, reaching 2.00-2.20 billion broilers, equivalent to total chicken outputs of 3.30-3.50 million tons, growing at the same rate of 2.5-3.5% annually. This growth will be driven by increased consumption demand both domestically and internationally. Domestic consumption is projected to grow by 1.5-2.5% per year, supported by (i) consumers continuing to seek affordable products, (ii) the health-conscious trend emphasizing high-protein, low-fat foods, (iii) the recovery of the tourism sector boosting the restaurant business, and (iv) lower animal feed costs leading to a decline in chicken prices both domestically and internationally. Export volume is expected to grow by 4.0-5.0% per year, driven by (i) trade cooperation with Middle Eastern and neighboring countries expanding export markets, (ii) consumers continuing to choose affordable protein amidst a slow global economic recovery, and (iii) low-fat chicken products catering to the health-conscious trend.
Beverage Industry: Production and consumption will benefit from restocking, while exports will improve with stronger border trade.
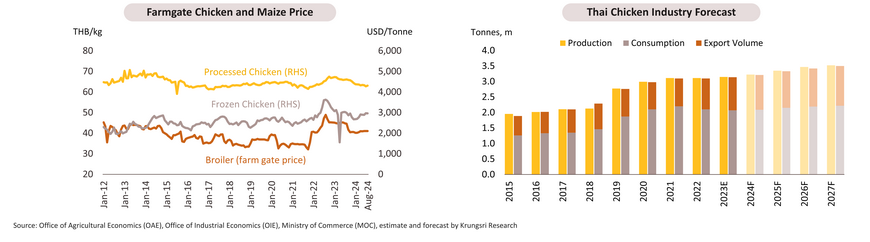
- Over 8M24, Thailand's beverage production expanded by 4.5% YoY, driven by the return to normal outdoor activities, the continuous recovery of the tourism industry, and the normalization of inventory levels for alcoholic beverages. Domestic sales volume grew by 4.2% YoY, supported by ongoing economic activity and rising numbers of foreign tourists, which have bolstered the recovery of restaurants and entertainment businesses. Additionally, hotter-than-usual weather, partially due to the El Niño phenomenon in 1H24, and a more diverse range of products that better meet consumer needs contributed to this growth. Export volume expanded by 2.0% YoY, aided by the recovery of business activity in key markets such as Vietnam, China, and Lao PDR. Export value grew by +8.6% YoY, driven by higher product prices resulting from increased raw material and transportation costs. For 2024, production is projected to grow by 4.5-5.5%, while domestic sales are expected to increase by 4.0-5.0%. This overall growth is driven by improving business activity and a rising number of tourists. Export volume is anticipated to grow by 1.0-2.0%, supported by the gradual recovery of key trading partners.
- Over 2025-2027, production volume is expected to grow by an average of 3.5-4.5% annually, driven by i) inventory restocking to meet recovering domestic demand and ii) the development of health-focused products. However, Increased raw material and packaging costs from the shift to eco-friendly products remain major headwinds. Domestic sales are projected to increase by 3.5-4.5% per year, supported by rising temperatures, ongoing growth in economic activity and the tourism sector, urbanization with an expansion of modern retail, and the growth of online sales channels and delivery services for non-alcoholic beverages. Export volume is expected to grow by 2.0-3.0% per year, mainly due to the gradual recovery of border trade with neighboring countries. However, increased investments by both Thai and foreign manufacturers in CLMV countries may limit export growth in certain segments, particularly in the beer beverage sector.
Housing (BMR): Revived sales are driven by real demand and foreign purchasing power.
-
In 8M24, the number of new housing units coming to market fell -37.3% YoY to 35,007 units. For condominiums and townhouses, new supply slumped by respectively -54.5% YoY and -28.3% YoY, but for detached houses, this jumped 8.8% YoY. Sales of new units crashed -65.1% YoY to just 7,478 units due to: (i) the slow growth of the Thai economy and high levels of household debt (at 89.6% of GDP in 2Q24) leading to a decrease in consumers' borrowing capacity; (ii) tighter lending conditions, especially for low- to middle-income borrowers; and (iii) rising interest rates since 2022 have increased cost burdens for consumers. These factors have led developers to delay the launch of new housing projects. For the rest of the year, a strong recovery in tourism is expected to boost demand for housing, particularly for properties priced at THB 5m and above popular with foreign buyers. Meanwhile, accelerated government spending since 2Q24 will somewhat help improve purchasing power. As a result, new project launches are expected to decrease by -20.0% for the entire year of 2024, while total sales will decline by -25.0%.
-
The market is likely to recover gradually in 2025-2027, supported by (i) the Thai economy's recovery, driven by increased public investment in transportation infrastructure, is expected to boost demand for housing along and near metro lines. Meanwhile, the tourism sector's rebound has increased demand from foreign buyers for second homes and investment properties; and (ii) government measures to promote investment will create more opportunities for expatriates to work in Thailand, increasing housing demand. However, the housing market faces risks from persistently high household debt, which undermines purchasing power and loan repayment ability, causing financial institutions to tighten lending conditions. In addition, the accumulation of unsold inventory in some areas has limited the ability to increase selling prices in line with rising costs. The supply of housing will continue to increase, especially for high-end properties to accommodate high-income customers.The housing market outlook can be summarized as follows:
-
The number of newly launched units is expected to increase by an average of 3-4% per year, from large developers with strong financial bases. These projects will focus on low-rise housing targeting upper-middle to high-income customers, who have strong purchasing power and are not significantly affected by economic uncertainties. Meanwhile, high-rise projects will expand along the railway routes.
-
Sales are expected to gradually recover at 1-3% per year, driven by real-demand customers with high purchasing power. The growth of the tourism sector and the return of foreign purchasing power will increase demand in the condominium market in central areas and along railway routes. Additionally, expanding railway services to cover more suburban areas, such as the Orange Line (Taling Chan-Min Buri, expected to open in 2025), will enhance the demand for housing in those locations.
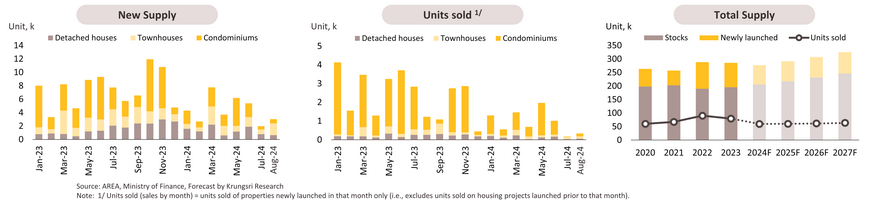
Office Building (BMR): The occupancy rate is expected to hit a record low, pressured by total supply outpacing demand.
-
In 1H24, the office rental market in the BMR continued to face pressure from excess supply, with 224,086 sq.m. of new space entering the market (up 66.3% YoY). Notable developments include One Bangkok Towers 3 and 4, the Supalai Icon Sathorn project, and the Ratchayothin Hill building. As a result, total supply expanded by 3.7% YoY to 9.7 million sq.m., while demand edged up just 0.2% YoY to 7.9 million sq.m. This led to a decline in the occupancy rate to 81.5%. Throughout the remainder of the year, more than 200,000 sq.m. of new office space is expected to enter the market, with demand gradually increasing as Thai companies expand their office space. This expansion enhances their image and attracts talented employees. Additionally, overseas players relocating production facilities to Thailand (e.g., Electric vehicles) are also contributing to this demand. For the year, the supply of rented office space is therefore forecast to rise by almost 450,000 sq.m, resulting in a 4.7% increase in accumulated supply. Meanwhile, demand for office rentals is expected to increase by 1.0%, or 80,000 sq.m., which is lower than the average of 140,000 square meters per year from 2017 to 2019. This gap will then result in a fall in the average occupancy rate to 80.1%, as well as a drop in rents, particularly for Grade A offices.
-
In 2025-2026, the office rental business is expected to improve in line with the recovery of the Thai economy, which is projected to grow around 3.0%. This will support business sectors, particularly services, by expanding employment. Demand for office space is thus anticipated to grow by 1.0-2.0% annually, particularly for Green Offices, which attract large corporations and international firms interested in enhancing their image in line with the ESG trend. However, the rise of hybrid workplace policies and the growing popularity of Co-Working Spaces are limiting demand for traditional office space. Meanwhile, office space supply is expected to increase by an average of 1.0-2.5% per year, mainly from large mixed-use projects that offer Grade A and A+ offices with green building standards. This will intensify competition in the market, giving tenants greater bargaining power and likely pushing the overall occupancy rate to drop to a historic low of 80%. As for rental rates, the trend will vary. Newly completed offices in the Central Business District (CBD) are expected to see stable or slightly increasing rents due to strong business demand. However, rents in other areas are likely to remain flat or decrease, particularly for older buildings.
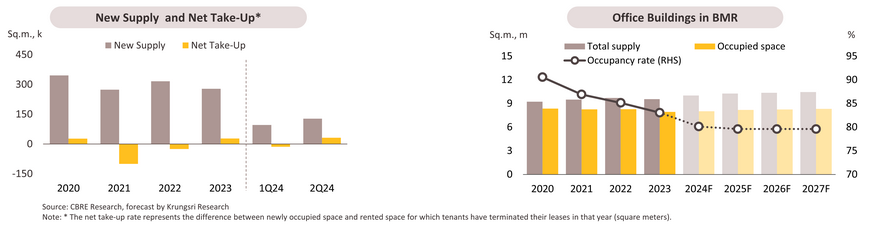
Industrial Estate: Land sales and leases continue to rise, driven by investment relocation.
-
In 1H24, land sales and leases totaled 4,017 rai, up 42.4% YoY, with the majority still concentrated in the Eastern region, covering 3,480 rai (87% of total land sales and leases nationwide), up 40.8% YoY. The Central region (including Bangkok and surrounding areas) followed with 485 rai (+83.0% YoY). As a result, total accumulated land sales and leases for 1H24 reached 133,000 rai, in line with the 34.9% YoY growth in investment promotion application value and the 26.9% YoY increase in investment approval value. On the supply side, no new industrial estates were established during 1H24, keeping the nationwide total at 68 estates, covering 173,000 rai, with an occupancy rate of 79.0%, an increase from 75.7% at the end of 2023. It is expected that land sales and leases in industrial estates will continue to grow in the remainder of the year, driven by recovery of investment activity, bringing total land sales and leases for the full year 2024 to 6,000 rai (+6.7%).
-
Over 2025-2027, land sales and leases are expected to see average growth of 7.0-8.0% per year, or approximately 7,000 rai annually, thanks to: (i) geopolitical issues contributing to increased investment relocation to ASEAN and Thailand, and (ii) progress on infrastructure megaprojects, especially in the EEC including deep-sea ports, such as phase 3 of the Map Ta Phut Port development (currently 80.9% complete) and phase 3 of Laem Chabang Port (29.0% complete) (source: EEC, 10 June 2024). Additionally, construction of the high-speed rail linking three airports is expected to begin at the start of 2025. The Eastern region continues to attract strong interest from investors due to its strategic location and government incentives offered under the EEC policy. For instance, Google plans to build its first data center in the WHA Industrial Estate in Chonburi. Developers will increasingly cater to the growing investment in smart industrial estates and BCG industries by focusing more on developing environmentally friendly industrial estate ecosystems. However, supply-side challenges include (i) insufficient land supply for large-scale investor projects due to restrictions of urban planning not aligning with investment areas, and (ii) delays in environmental impact assessments (EIA) for industrial estate projects.
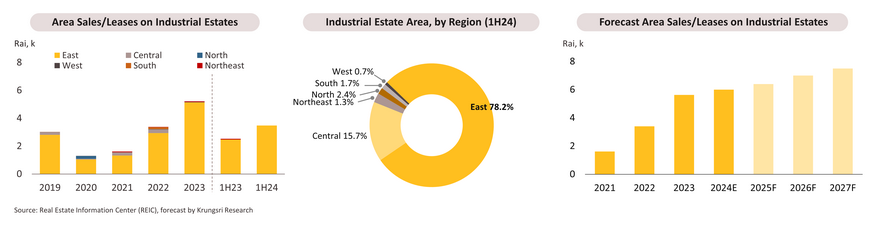
Construction: Construction investment value in 2024 is expected to contract, with gradual recovery anticipated in 2025-2027
-
Overall construction investment contracted -11.2% YoY in 1H24 due to the delayed passing of the 2024 budget, which then triggered a -19.3% YoY slump in public construction investment, though this especially affected work on infrastructure megaprojects (down -23.2% YoY). This came despite the 1.2% increase in private construction investment driven by non-residential construction that rose 6.7% YoY. Meanwhile, residential construction investment contracted -3.2% YoY. For the remainder of the year, public construction is expected to improve following the disbursement of budgets for some ongoing infrastructure projects. Throughout 2024, the overall construction investment is forecast to slip by between -2.0% and -3.0%.
-
Between 2025-2027, the total construction investment value is anticipated to return to an average annual growth of 4.5-5.0%. Work on both ongoing and new projects especially those related to the development of multimodal transport networks will accelerate, and this will then crowd in greater private construction investment in adjacent locations. Megaprojects in the EEC areas are expected to continue steadily with expedited projects including (i) stage 1 of phase 3 of the Map Ta Phut Port development project; (ii) phase 3 of the Laem Chabang port development; and (iii) the delayed high-speed three-airport rail-link, for which ground should be broken in 2025. For other strategic locations, the megaprojects that will commence in 2025 include (i) entertainment complexes, with 10% of total site areas reserved for casinos (costing THB 300-500bn) and (ii) the Gulf of Thailand Pearl Necklace project, which is a seawall that will help to reduce coastal erosion, alleviate flooding in Bangkok, and establish new investment zones.
Hotel: Foreign tourists in Thailand grew 30.1% YoY over 9M24, with projections to reach 35.6m, 40m, and 45m in 2024, 2025, and 2027 respectively.
-
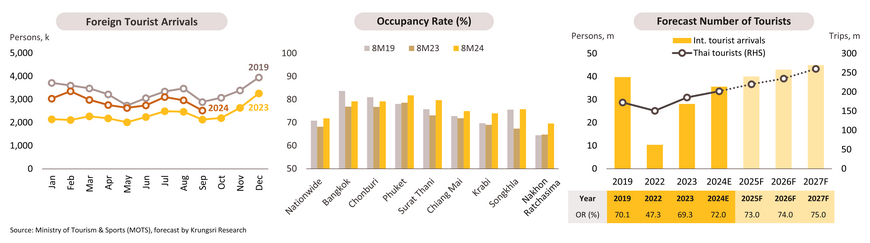
Through 9M24, foreign tourist in Thailand continued to grow, but remained lower than the pre-COVID level. 26.1m foreign arrivals were recorded with a +30.1% YoY growth, led by the 3 main markets including China (5.2m arrivals), Malaysia (3.7m), and India (1.5m). However, international tourists still accounted for merely 88% of 9M19. Chinese tourist numbers have only reached 61% of 9M19 levels, constrained by limited flights, higher airfares, weaker purchasing power, and a policy favoring domestic tourism amid China’s economic slowdown. Meanwhile, Thai domestic tourists rose 9.3% to 100.1m trips in 1H24, supported by stimulus measures to promote tourism in secondary provinces. The nationwide occupancy rate (OR) climbed to 71.8% in 8M24. Increases in occupancy and average daily rates (ADR) in 8M24 led to significant growth of 41.5% YoY in revenue per available room (RevPAR) compared to 8M19. Throughout 2024, tourist arrivals are forecast to increase 26.5% to 35.6m (still lower than the pre-COVID level of 39.9m), with Chinese tourists expected to reach 7.5m. Domestic tourists are forecast to record 202.0m trips (+9.0%). The national OR is expected to average 72%, surpassing 70.1% in 2019, with key tourist destinations such as Bangkok, Chonburi, and Phuket expected to see rates rise to 80%.
-
From 2025 to 2027, foreign tourist arrivals are forecast to reach 40, 43, and 45m, respectively. Chinese and Malaysian tourists will remain key markets, followed by other high-potential markets including ASEAN countries and Eastern Europe. Chinese tourists are expected to reach 11m in 2025 (the same as 2019 levels) and increase to 15 million by 2027, driven by visa-free measures and ongoing tourism promotion activities between Thailand and China. Thai domestic tourists are forecast to make 220m trips (+8.9%) in 2025 and will likely reach 260m trips (+10.6%) in 2027. Nationwide occupancy rates are projected to range between 73-75% from 2025 to 2027.
Private hospital: Revenue tends to grow steadily from increasing demand for medical services, while businesses invest in new innovations and technologies to attract patients.
-
During 9M24, hospital business growth mirrored pre-COVID-19 levels, driven by the resumption of normal business activities and the seasonal peak in Q3 (rainy season), which boosted patient numbers for monitored illnesses like influenza (+239.2% in 1H2024). Moreover, hospital revenues were strengthened by the gradual return of foreign patients, reflected by 26.1 million tourists, including medical tourists, particularly from the Middle East. Trends in preventive healthcare also increased demand for in-depth check-ups. Private hospitals expanded specialized services, adopted advanced technologies like stem cell therapy, and opened branches in tourist hotspots and the EEC (e.g., Sriracha and Rayong). For the remainder of the year, improved Thai economic conditions, an increase in overseas patients, and the resumption of Kuwaiti patient referrals will further drive growth. Overall, private hospital revenue is expected to grow by 9-10% in 2024 compared to 2023.
-
For 2025-2027, the business is expected to be supported by: (i) Thailand as an aged society, with 20% of the population over 60 in 2024, leading to increased healthcare spending; (ii) a rise in foreign patients, including medical tourists, aligned with expected tourist numbers exceeding 40 million by 2025; (iii) increasing preventive healthcare trends driven by high treatment costs relative to income; and (iv) increased investments by private hospitals to expand branches and services (e.g., treating complex diseases and developing Quaternary Care) and adopt new technologies to attract patients. However, a slow domestic economic recovery may lead to cautious spending, and prolonged unrest in the Middle East could affect patient numbers from that region. Private hospital revenues are projected to grow at an average annual rate of 10-12%.
Modern trade: Revenue is gradually increasing due to the slow recovery of purchasing power among vulnerable groups.
-
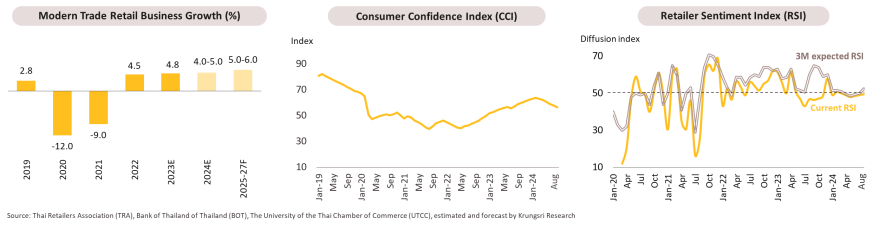
During 8M24, income grew gradually due to (i) the recovery of the tourism sector, which boosted demand for consumer goods, particularly food, beverages, and essentials, (ii) the government’s stimulus measures, such as Easy-E receipt, and (iii) continued expansion of business operators in Bangkok and other provinces, like Robinson Lifestyle in Nong Khai and Nakhon Phanom. However, revenue growth remains constrained by the fragile purchasing power of middle- and lower-income consumers. The Consumer Confidence Index dropped to 56.5 in August from 63.8 in February due to persistently high household debt (89.6% of GDP in Q2) and intense competition from numerous online retailers. For the rest of the year, the business is expected to improve due to the onset of the tourism high season and the year-end festive period, as well as stimulus measures through digital wallet programs. Throughout 2024, income growth is projected to be 4.0-5.0%, similar to 4.8% in 2023.
-
For 2025-2027, the business is expected to grow by 5.0-6.0% annually, helped by: (i) a gradual recovery in domestic purchasing power following economic expansion; (ii) the return of foreign tourists, which will boost spending, particularly in tourist destinations; (iii) progress in developing public infrastructure projects and the new (draft) Bangkok City Plan, encouraging retailers to accelerate branch expansion to accommodate urban community growth; (iv) sales promotions through omnichannel platforms; and (v) economic growth in neighboring countries, benefiting retailers in border provinces and major cities in the region. Sales of supermarkets and convenience stores are expected to grow steadily, as they offer essential consumer goods and continue to expand their branches. However, growth in discount stores and hypermarkets may slow, as most customers are in the middle-income group and below, whose purchasing power is recovering slowly. Department store sales are anticipated to recover gradually, though consumers remain cautious about spending on non-essential items.
Air Passenger Services: Businesses have benefited from the ongoing recovery in tourism and supportive government measures.
-
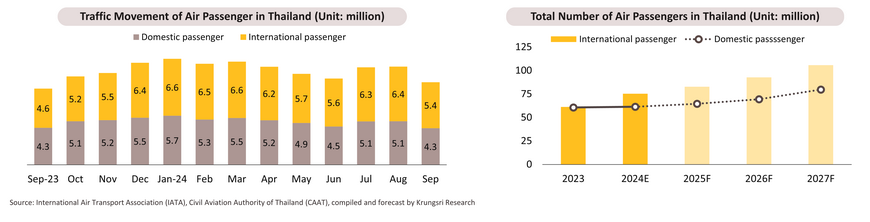
In 9M24, Thailand’s air passenger numbers grew by 13.1% YoY, split between a 25.3% rise in international travelers and a 1.0% increase in domestic passengers. Key factors included rising tourism demand, with international arrivals up by 30.1% YoY (26.1mn) and domestic travel up 9.3% YoY (100.1mn trips in 6M24). Growth was also driven by initiatives such as visa exemptions for 93 countries, stay extensions, increased routes and frequencies from key markets like India, tax incentives in 55 secondary provinces (May 1 - Nov 30, 2024), and airport discounts for airlines (Nov 1, 2023 - Oct 31, 2025). For the rest of the year, the industry is expected to continue growing as peak travel season approaches, with airlines expanding routes and frequencies for events like the Harbin Ice & Snow Sculpture Festival in China and the Sapporo Snow Festival in Japan. For 2024, total passenger numbers are forecast to grow by 12.2%, with international and domestic passengers rising by 26.0% and 1.5%, respectively.
-
For 2025-2027, the air passenger service is expected to grow steadily, supported by (i) a global tourism recovery, with Bain & Company predicting the market to exceed USD 17bn by 2027. IATA projects a 7.2% annual growth in passenger numbers in APAC, outpacing the 5.0% global average. Thailand’s tourism is expected to surpass pre-pandemic levels from 2025, driven by health projects like the "Phuket Wellness Hub“ and sports tourism initiatives such as marathons and racing events; (ii) codeshare agreements boosting long-haul passenger numbers (e.g., Thai Airways with Gulf Air and Bangkok Airways with Lufthansa and Swiss International Airlines); (iii) collaboration among Thailand, China, Laos, and ICAO expected to expand cross-border flight routes to accommodate increasing air traffic; and (iv) infrastructure enhancements benefiting airlines through increased flight frequency and passenger handling (e.g., the expansion of the parking at Hua Hin Airport (completion in 2025) and the opening of the 3rd runway at Suvarnabhumi Airport (scheduled for Nov 1, 2024)). These will drive annual passenger growth of 13-15%, with international routes increasing by 10-12% and domestic routes by 9-10%. However, challenges remain, including (i) persistently high jet fuel costs raising ticket prices; (ii) rising competition (e.g., the launch of the Ho Chi Minh City-Vientiane route connecting to various Asian and Eastern European countries); and (iii) geopolitical tensions potentially leading to flight cancellations or reductions.
Sea freight services: Demand is expected to outpace the supply growth, keeping freight rates above pre-COVID-19 levels.
-
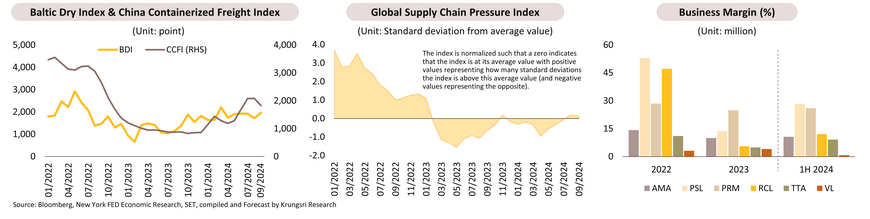
In 8M24, the business grew by 4.6% YoY, in line with Thailand's international trade growth, driven by a 5.0% YoY increase in imports and a 4.2% YoY rise in exports. Global droughts, floods, and geopolitical conflicts, especially attacks on cargo ships in the Red Sea and Suez Canal, led to increased stockpiling and higher shipping costs. This is reflected in a 59.7% YoY increase in the China Containerized Freight Index (CCFI) and a 57.5% YoY rise in the Baltic Dry Index (BDI) for 9M24. Additionally, the Global Supply Chain Pressure Index indicates heightened pressure. The remainder of the year is expected to see continued demand growth due to year-end spending, domestic economic stimulus measures (e.g., cash handouts to vulnerable groups), and accelerated US and EU imports from China before potential tariff increases in September and November 2024. These factors are likely to boost demand for consumer products, raw materials, and intermediate goods from Thailand. Throughout 2024, the container shipping industry’s revenue is projected to grow 7-9%, rebounding from a -48.6% contraction in 2023, while bulk shipping revenue is expected to rise by 25-27% recovering from a -16.8% decline in 2023.
-
Over 2025-2027, Thailand's sea freight demand is expected to grow by 3-5% per year, up from 2.5% in 2023. This growth is attributed to continued economic expansion in major trade partners like ASEAN and China, with the IMF forecasting annual growth rates of 4.5% and 4.1%, respectively, from 2025-2027. Furthermore, the projected average growth of Thailand's economy of 3.0% per year and the ongoing expansion of e-commerce will boost consumer demand. However, geopolitical conflicts continue to create uncertainty, and the demand of vessels is expected to grow in tandem with supply. According to BIMCO estimates, the demand for container vessels is expected to increase by 3.5-4.5% YoY, while global fleet is projected to grow by 4.0-5.0% YoY. For bulk carriers, Clarksons anticipates limited fleet expansion due to constraints in shipyard capacity. As a result, freight rates are projected to remain above pre-COVID levels, and thus, annual revenue growth for container and bulk carriers is forecast at 4-6% and 3-5%, respectively.
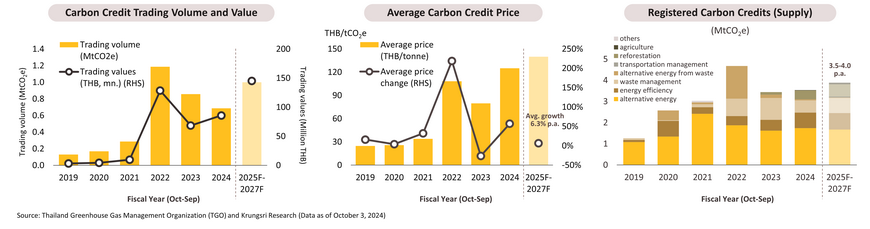
Carbon Credits: The market expansion is driven by increasingly stringent domestic and international green regulations.
- In FY2024 (Oct 2023 - Sep 2024), the trading volume of carbon credits under the Thailand Voluntary Emission Reduction Program (T-VER) was 0.7 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent (MtCO2e), with a total trading value of THB 85.8mn. (+25.6% YoY) and an average price of THB 125 per tCO2e (+56.9% YoY). Purchases were driven by large organizations, particularly Kasikorn Bank, Double A, Lion Corporation, Precious Shipping PCL, and Siam Piwat. On the supply side, the volume of registered carbon credits was 3.5 MtCO2e (+2.6% YoY). Most of these credits involve the development of alternative energy sources (49%), energy efficiency (21%), waste management (16%), and reforestation (12%).
- In FY2025-FY2027, the supply of carbon credits is expected to slightly increase from the FY2024 level to approximately 3.5-4.0 MtCO2e per year on average, with more credits being sourced from nature-based solutions, as large businesses like SCG and Mitr Phol invest more in carbon credit projects related to reforestation and agriculture. Moreover, rising demand is anticipated, likely driving prices and trading value above those observed in FY2024. The total annual purchases of credits are expected to average around 1.0 MtCO2e (+20.8% p.a.). Supporting factors include: (i) more organizations striving for net-zero goals, and (ii) the development of domestic laws, such as the Climate Change Act and Carbon Tax, along with stricter green measures by Thailand’s trade partners, which will accelerate carbon market expansion. However, the key challenge lies in doubts surrounding the integrity and quality of Thai carbon credits compared to international standards, such as Core Carbon Principles (CCPs) and CORSIA-eligible credits.
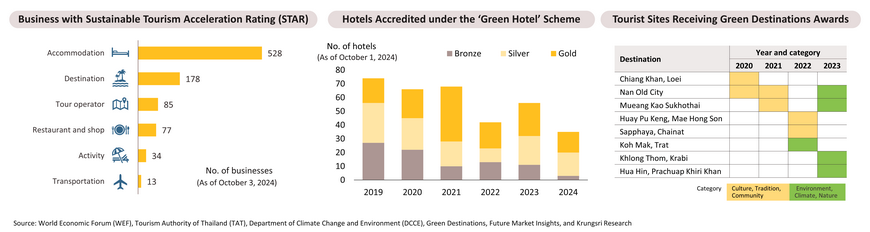
Sustainable Tourism: The industry is poised for growth amid rising demand from green travelers, but businesses will face stricter environmental and social standards.
-
Sustainable tourism, which aims to minimize social and environmental impacts while generating economic benefits for all stakeholders, has been gaining momentum globally. Environmentally, it emphasizes biodiversity preservation, renewable energy use, and reducing single-use plastics. Although Thailand's sustainable tourism competitiveness lags behind many other countries, the government is developing sustainable tourism models such as Koh Mak, encouraging businesses to measure-reduce-offset their carbon emissions, and supporting the adoption of sustainability standards like Green Hotel Certification, the Sustainable Tourism Acceleration Rating (STAR) Program, and Green Destinations. However, certified businesses and destinations still represent only a small portion of the overall industry.
-
The Thai sustainable tourism industry is expected to grow in line with global trends. According to Future Market Insights, the Thai market values will increase from USD 33.2mn. (about THB 1.1bn.) in 2024 to USD 143.9mn. (around THB 4.9bn.) in 2034, with an average annual growth rate of 15.8%. This growth will likely be driven by rising consumer environmental concerns, as a Booking.com survey shows that three-quarters of tourists aim to travel more sustainably, while an Agoda survey reveals that around 80% of Asian tourists prefer purchasing sustainable travel packages. Additionally, the establishment of official net-zero goals at both organizational and national levels will contribute to this trend. Thai businesses, including hotels, restaurants, and transportation providers, aiming to seize opportunities in eco-conscious markets may face challenges in adopting stricter environmental and social standards, as well as sustainability transition costs.

La Niña will run from Q3 2024 through the start of 2025, keeping rainfall above average and bringing reservoir levels remain high in 1H25
Thailand has moved rapidly from El Niño-induced drought in 1H24 to flood conditions in 2H24. Indicators of these changes can be seen in: (i) the swing in the Oceanic Nino Index (ONI) to neutral and then to La Niña conditions, and with this the onset of greater than average rainfall; (ii) the influence of annual tropical storms; (iii) the fall in the PDO and IOD indices, which are moving to a negative phase (i.e., below -0.5), representing the increasing influence of storms; and (iv) the Monsoon Index moving to nearly normal range in short-terms, indicating heavy rainfall in the surrounding areas of Thailand.

In 2024, flood area covering northern, central, northeastern and parts of the south, resulting in expected losses of THB 46.5 bn, and a -0.27% reduction in nominal GDP.
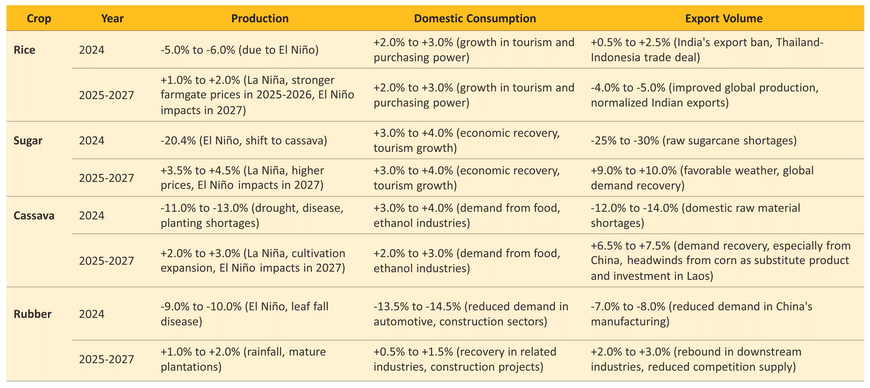
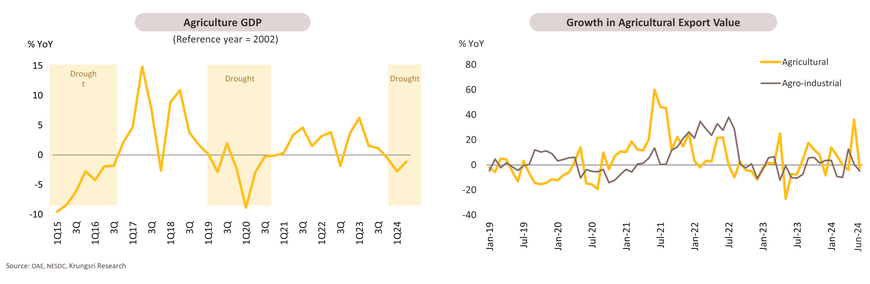
In 1H24, agriculture GDP and agro-industries contracted due to the impacts of El Niño, despite an increase in export value driven by rising prices.
-
In Q1 and Q2 2024, agriculture GDP contracted by -2.7% and -1.1% YoY, respectively, due to i) reduced rainfall and higher temperatures from El Niño, leading to crop damage; ii) still-high production costs, which led farmers to cut spending on yield improvements; iii) the impacts from disease and pest; and iv) reduced cultivation activity leading to a contraction in agricultural-related services. However, in 2H24, agricultural GDP is expected to grow by 0.2-1.2% supported by more favorable weather conditions from the onset of La Niña.
-
In 1H24, total agricultural and agro-industrial export value increased by 3.3% YoY, driven by 48.1% YoY growth in rice export value and 7.6% YoY growth in agricultural products. This was due to India’s export suspension and global concerns over food security caused by natural disasters and war that boosted global demand. Rubber and processed chicken also saw growth in export value of 30.6% YoY and 6.2% YoY respectively. In contrast, agro-industrial export value declined -1.9% YoY, mainly due to a -37.5% YoY drop in sugar exports, caused by a drought-induced supply shortage, and a decline in vegetable fats and oils (-20.1% YoY) as well as canned and processed vegetables (-9.1% YoY).
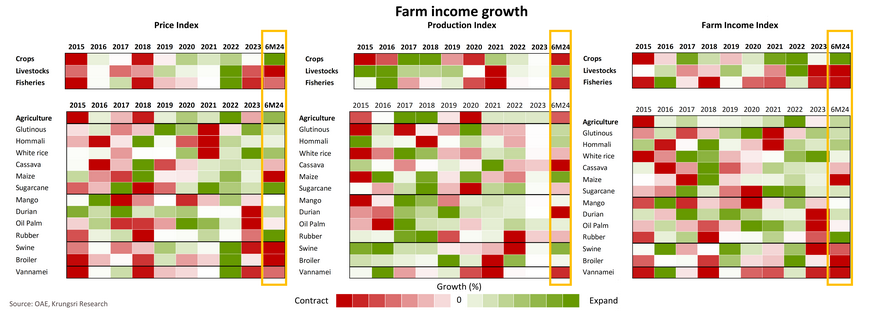
6M24, crop farmers' income grew, in contrast to a decline in livestock farmers' income, primarily driven by price effects.
-
In 1H24, crop production (rice, sugarcane, oil palm, rubber, and fruit) contracted by -2.4% YoY due to the impact of El Niño and disease outbreaks, particularly affecting rice, sugarcane, durian, and rubber. However, crop prices surged by 15.7% YoY due to sustained demand amid decreasing supply, leading to a 9.4% YoY increase in income for crop farmers.
-
Meanwhile, livestock production increased by 5.3% YoY due to improved farm management practices for disease prevention in pig farming and expanded chicken production to meet expected market recovery. However, domestic demand declined due to weak purchasing power with high living costs, leading to excess supply and a decline in livestock prices by -13.3% YoY. This resulted in income declines of -13.4%, -8.7%, and -5.1% YoY for pig, broiler, and cattle farmers, respectively.
In 2024, El Niño will reduce production and affect exports, but La Niña, favorable weather and usable water in 2025-2027 will boost growth in agriculture and agro-industry.
Favorable weather and usable water due to La Niña will boost growth in agriculture outputs during 2025-2026, though the drought impacts will probably return in 2027.





.webp.aspx)